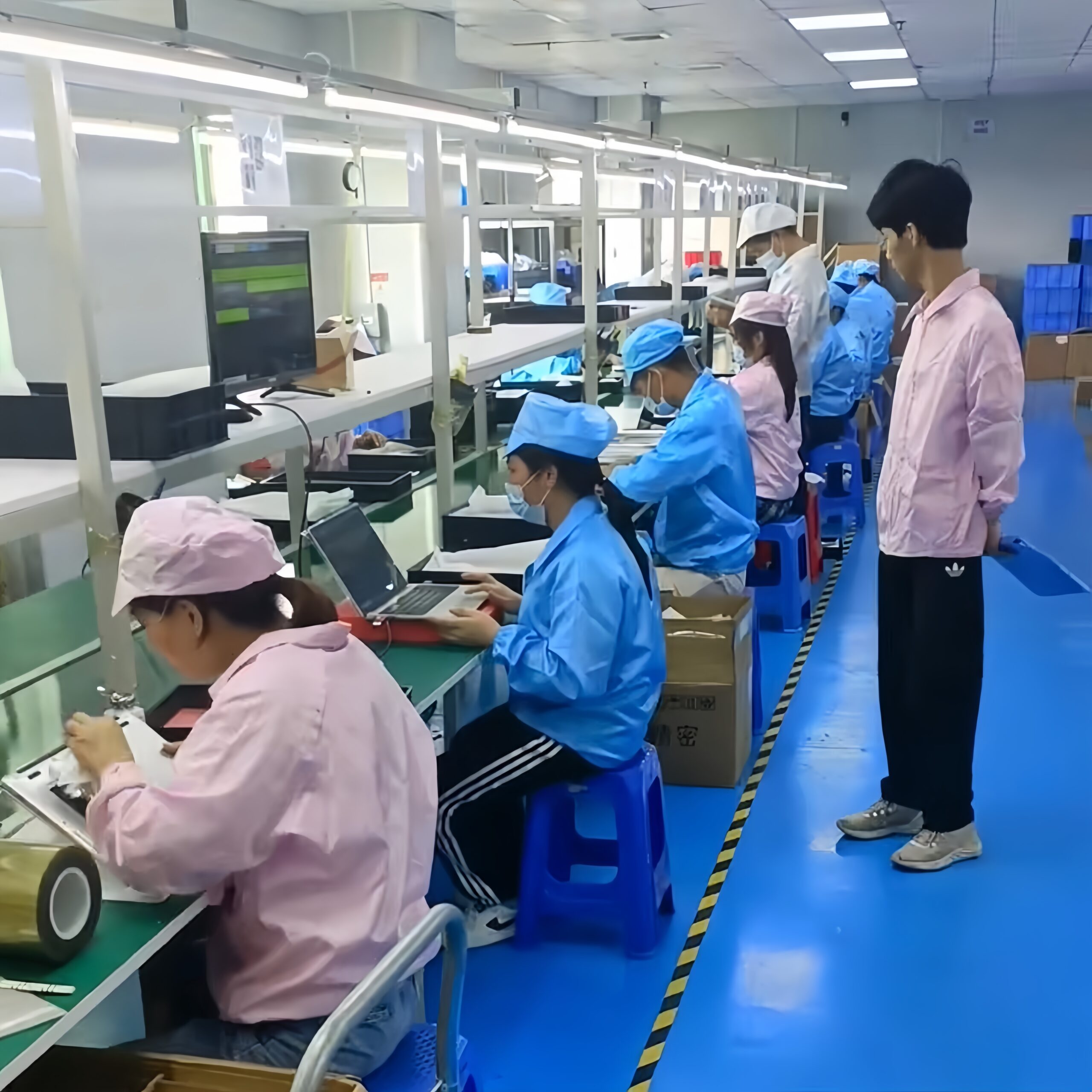
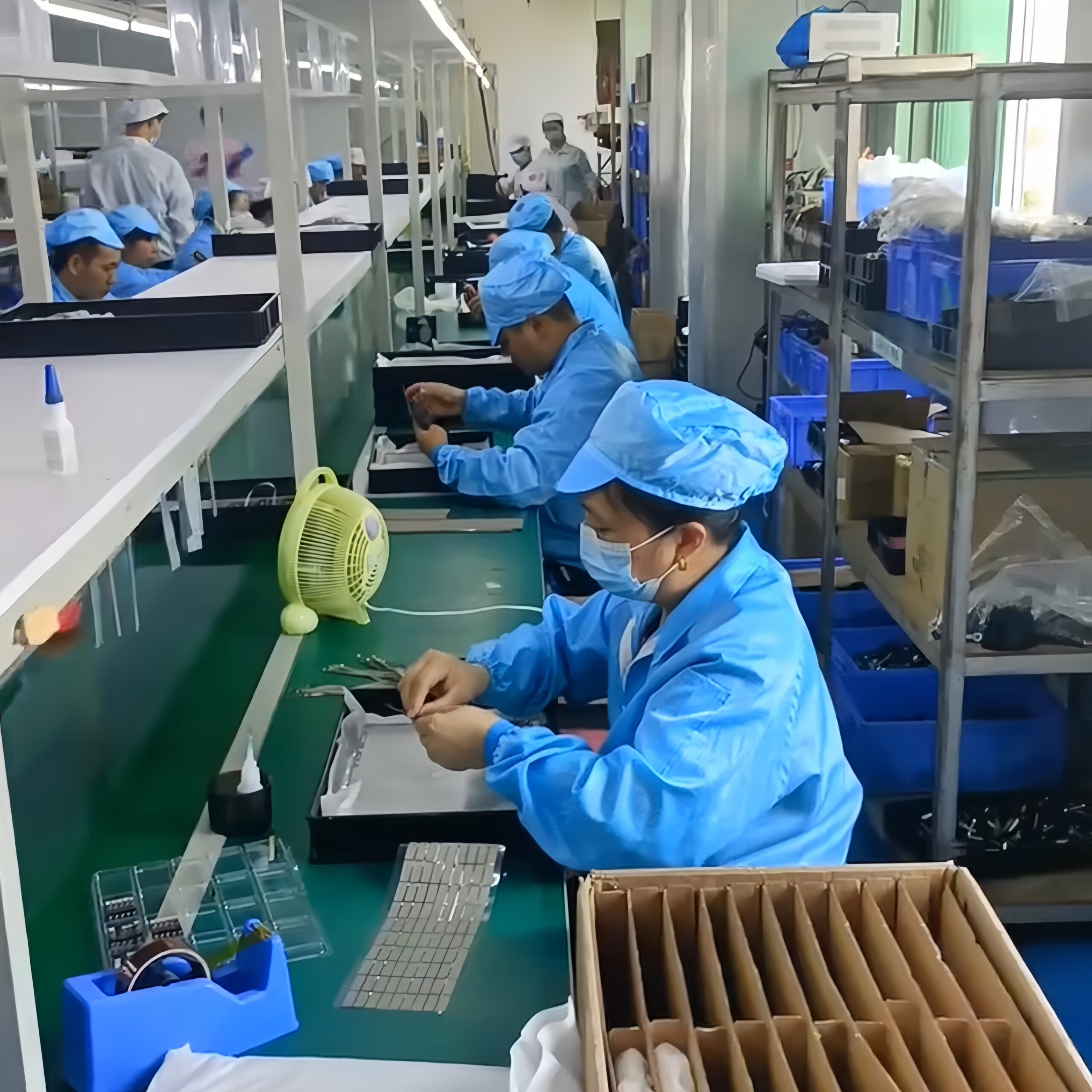
The following is a complete process scheme for the quality inspection of recycled laptops, covering all links from receipt to final evaluation. All our devices pass all the following test stages.
Preparation stage
1. Establish quality inspection standards
Establish clear quality inspection standards, including indicators such as appearance, function, and performance, to ensure evaluation consistency:
-Appearance inspection standards (scratches, damage, etc.).
-Hardware testing standards (CPU, memory, hard disk performance, etc.).
-Software function testing (operating system operation, driver installation, etc.).
2. Prepare quality inspection tools
-Hardware testing equipment: power adapter, hard disk testing tool, CPU testing tool, etc.
-Software tools: hard disk speed test software, stress testing software (such as AIDA64), battery health test tool, etc.
-Cleaning tools: alcohol cotton cloth, compressed air can, small screwdriver set.
3. Work area layout
Ensure that the work area is clean and tidy, and equipped with anti-static measures (such as anti-static wrist strap).
Receipt registration
1. Equipment registration
– Record the equipment model, serial number, and specifications (such as memory, hard disk capacity, graphics card model, etc.).
– Take photos of the equipment appearance, focusing on checking whether there are obvious defects on the appearance.
2. Preliminary classification
– Classify by equipment source (customer returns, recycling platforms, etc.).
– Roughly group by configuration, usage time, etc.
Quality inspection process
1. Appearance inspection
**Screen**: Check for cracks, bad pixels, bright spots.
**Body**: Check for scratches, deformation, breakage, etc.
**Interface**: Check whether the USB, HDMI, and power interfaces are loose or damaged.
**Keyboard and touchpad**: Check key integrity and touchpad sensitivity.
2. Hardware function inspection
**Battery and power**:
– Test battery health (charge times, remaining capacity).
Check whether the charger is working properly.
**Screen display**: Check brightness, contrast, and color consistency.
**Hard disk detection**: Use software (such as CrystalDiskInfo) to check the read and write speed and health status of the hard disk.
**Memory and CPU**: Run stress test software to check performance and stability.
**Cooling system**: Run high-load tasks to check fan noise and heat dissipation capacity.
**Wireless connection**: Test whether Wi-Fi and Bluetooth modules are working properly.
3. Software function inspection
Check whether it can be successfully started and enter the operating system.
Verify the integrity of the driver installation.
Check built-in software features (e.g. camera, microphone, audio playback).
Rating and classification
Rating and classification of equipment according to quality inspection results:
1. Rating
– Grade A: good appearance, normal function, excellent performance.
– Grade B: slight scratches or aging on the appearance, normal function.
– Grade C: obvious appearance defects or partial functional defects.
2. Classification and processing
– Equipment that can be directly resold.
– Equipment that needs repair or replacement of parts.
– Equipment that is scrapped or disassembled for recycling.

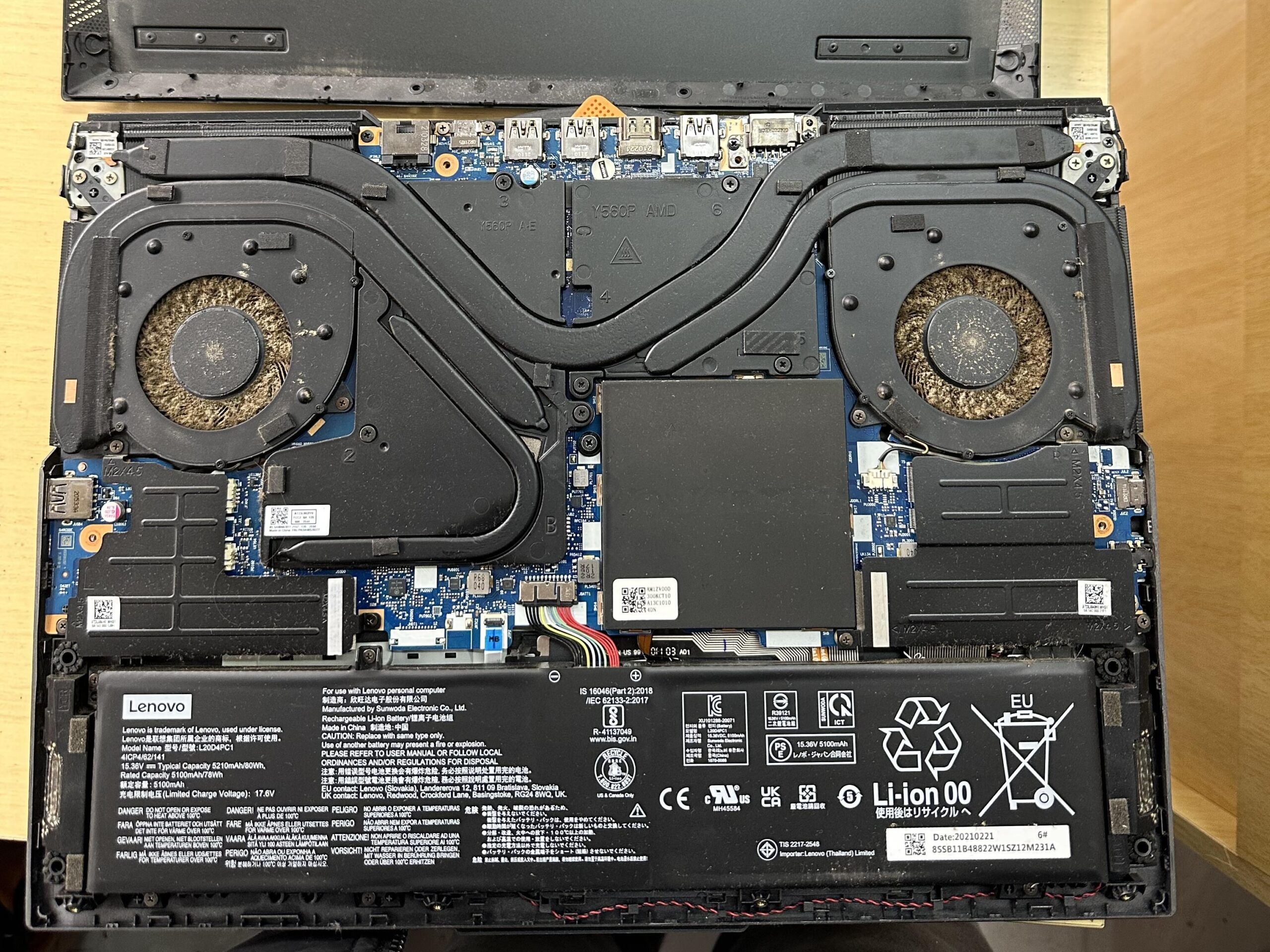
Cleaning and Maintenance
1. External cleaning: Use alcohol cotton cloth to clean the body and screen.
2. Internal cleaning: Open the back cover to clean the internal dust and replace the thermal grease if necessary.
3. Accessory inspection: Confirm the integrity of accessories such as power adapter and data cable.
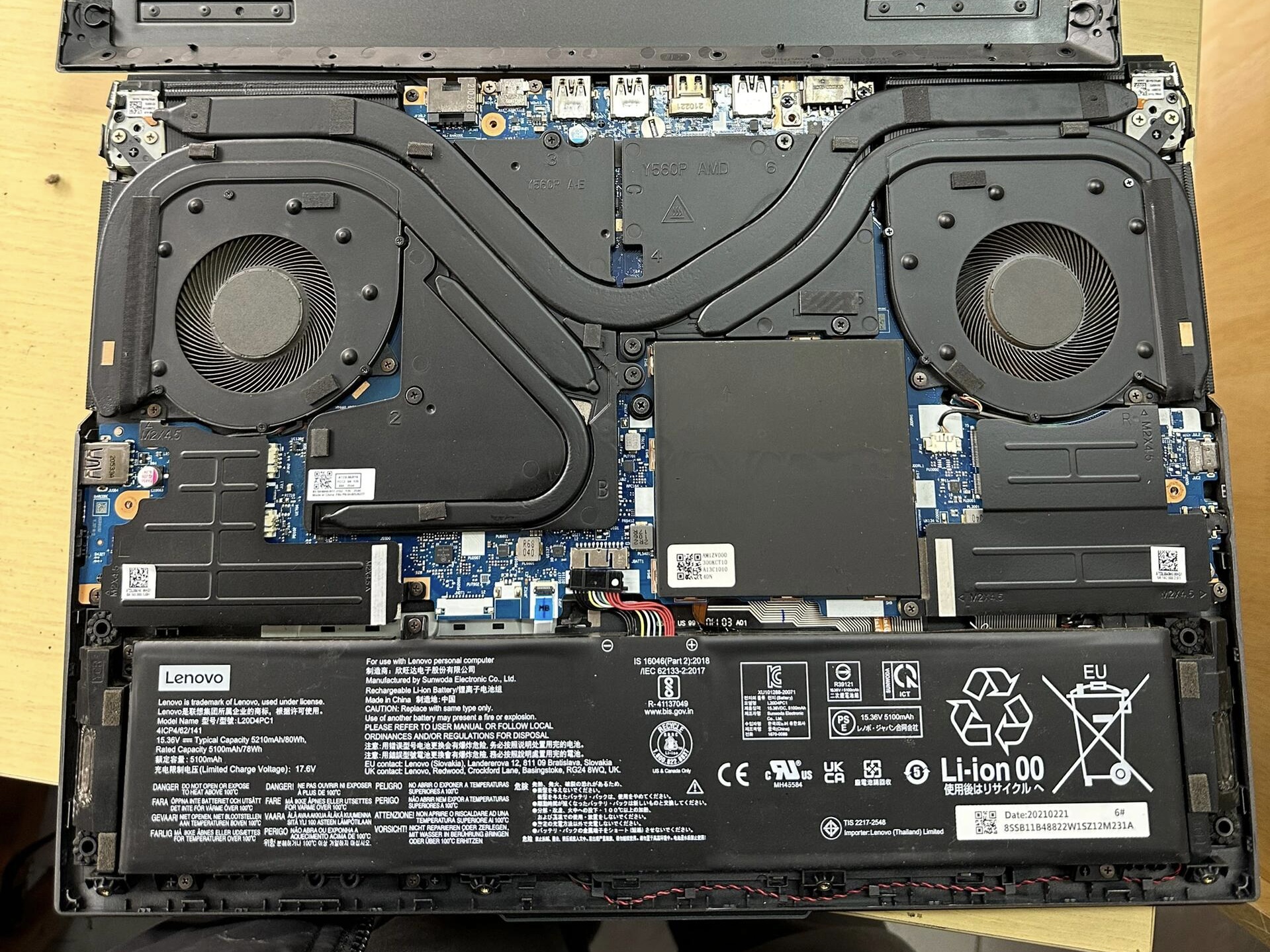

Data Processing
1. Data Clearance:
– Use professional software (such as DBAN) to completely clear the hard disk data.
– Reinstall the operating system to ensure that there is no privacy risk on the device.
2. Restore to factory settings: Ensure that the device can start normally and the software running environment is clean.
Reporting and Decision-making
1. Quality Inspection Report Generation
– Summarize the quality inspection results of the equipment, including detailed photos, performance evaluation and recommendations.
– Mark repair recommendations (if any) and resale price estimates.
2. Decision-making
– Decide how to deal with the equipment (resale, repair, disassembly and recycling, etc.).
– Update inventory information.
Subsequent processing
1. Repair equipment processing
-Replace damaged parts.
-Update device drivers and systems.
2. Resale equipment packaging
-Equipped with a full set of accessories and clean packaging.
-Print quality inspection certificate.
3. Disassembly and resource recycling
-Disassemble scrapped equipment and recycle valuable parts (such as memory sticks, hard drives).



Quality inspection and quality control
1. Sampling re-inspection
After each batch of quality inspection is completed, some equipment will be randomly selected for secondary quality inspection to ensure the accuracy of the results.
2. Improvement and optimization
For problems found in quality inspection, optimize the process flow and improve detection efficiency and accuracy.
Personnel arrangement and training
1. Position arrangement
-Appearance inspector, hardware tester, software tester, cleaner and other positions have clear division of labor
2. Skill training
-Regularly train quality inspectors to improve their ability to diagnose hardware and software problems.